Blog
The Importance of Treating Bed Sores for the Elderly and Inpatients
Bed sores, also known as pressure ulcers or decubitus ulcers, are a significant health concern for the elderly and hospitalized patients. These painful wounds can lead to serious complications, including infections and prolonged hospital stays. This document explores the importance of treating bed sores, emphasizing prevention, early detection, and effective management strategies to enhance the quality of life for vulnerable populations.

Understanding Bed Sores
Bed sores occur when there is prolonged pressure on the skin, often in areas where bones are close to the skin’s surface, such as the heels, hips, and tailbone. Factors contributing to their development include immobility, poor nutrition, and moisture from incontinence. For the elderly and inpatients, the risk is heightened due to decreased mobility and overall health challenges.

The Impact of Bed Sores
-
Physical Pain and Discomfort: Bed sores can cause significant pain, leading to decreased mobility and increased dependency on caregivers.
-
Infection Risk: Open wounds from bed sores can become infected, leading to serious complications such as sepsis, which can be life-threatening, especially in elderly patients.
-
Extended Hospitalization: The presence of bed sores can prolong hospital stays, increasing healthcare costs and burdening both patients and healthcare systems.
-
Psychological Effects: The discomfort and stigma associated with bed sores can lead to anxiety and depression in patients, further impacting their overall well-being

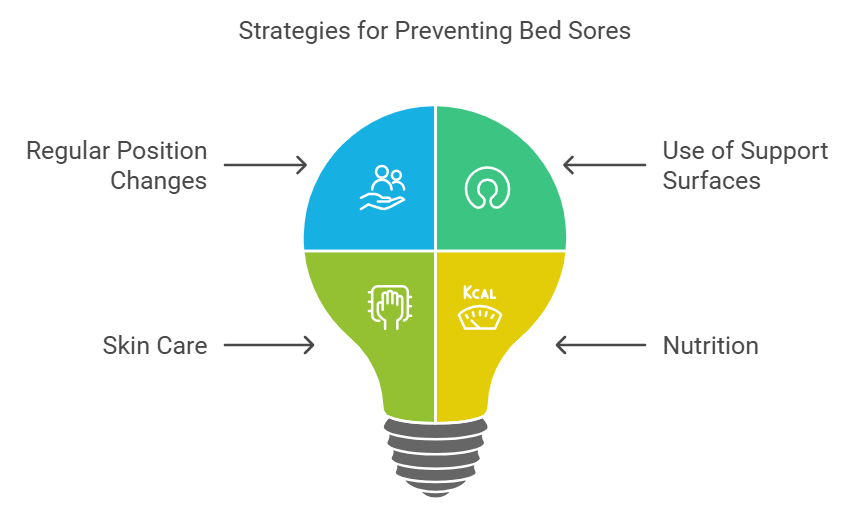
Prevention Strategies
Preventing bed sores is crucial for maintaining the health of elderly and inpatient populations. Key strategies include:
-
Regular Position Changes: Patients should be repositioned every two hours to relieve pressure on vulnerable areas.
-
Use of Support Surfaces: Specialized mattresses and cushions can help distribute weight more evenly and reduce pressure.
-
Skin Care: Keeping the skin clean and moisturized can prevent breakdown. Regular assessments of skin integrity are essential.
-
Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals supports skin health and aids in healing.
Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection of bed sores is vital for effective treatment. Caregivers should be trained to recognize the early signs of pressure ulcers, which may include:
-
Redness or discoloration of the skin
-
Warmth or swelling in the affected area
-
Pain or tenderness
Once identified, treatment options may include:
-
Wound Care: Cleaning the wound and applying appropriate dressings to promote healing.
-
Debridement: Removing dead tissue to facilitate healing.
-
Antibiotics: In cases of infection, antibiotics may be necessary to treat the underlying issue.
-
Pain Management: Addressing pain through medication or alternative therapies to improve patient comfort.
Conclusion
The treatment and prevention of bed sores are critical for the health and well-being of the elderly and inpatients. By implementing effective prevention strategies, promoting early detection, and providing appropriate treatment, caregivers can significantly reduce the incidence of bed sores and improve the quality of life for these vulnerable populations. It is essential for healthcare providers, families, and caregivers to work together to ensure that the risks of bed sores are minimized and managed effectively.

